Authors
Published
18 Feb 2022Form Number
LP1562PDF size
6 pages, 158 KBAbstract
This article highlights the enhancements Lenovo systems with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and Intel Optane PMem 200 series provide over previous generation systems with 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and Intel Optane PMem 100 series and over systems with only DRAM.
Introduction
This article was initially created by Krishna Yalamanchi, Cloud Solution Architect at Intel. His blog can be found here.
With the release of the 3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, Intel also introduced the 2nd Generation Intel® Optane™ persistent memory, or Intel Optane PMem 200 series. The combination of new processors and persistent memory provide:
- 8 memory channels with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors vs. 6 memory channels with 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- More powerful cores with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- 32% more Bandwidth in the Intel Optane PMem 200 series vs. the Intel Optane PMem 100 series
Customers look to Intel Optane Persistent Memory to:
- Lower TCO
- Protect against unplanned downtimes
- Simplify architectures with increased memory density
In this article, we want to highlight new performance metrics for Intel Optane PMem 200 series that bring greater value to customers' applications and workloads.
Highlights -
TCO for 2nd Generation Intel Optane persistent memory
- 34% Lower Cost Per Terabyte for SAP HANA™ for On-Prem Systems using 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors
Performance comparison between 1st and 2nd generation
- 99.4% for Phase 1 and Phase 2 SAP BWH Benchmarks compared to all DRAM system using Intel Optane PMEM 100 Series
- Double the performance for Phase 1 and Phase 2 SAP BWH benchmarks compared to 1st generation Intel Optane PMem 200 series
- 32% more bandwidth with PMem 200 series and powerful 3rd Generation Xeon Scalable processors leads to faster Phase 2
Increased Memory Density
- 6 TB of SAP HANA database using 2s PMem 200 series and powerful 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors
Comparing Intel Optane PMem 100 and 200 series with the SAP HANA BWH benchmark
Intel Optane PMem encrypts data stored in the SAP HANA database. It also increases memory density which allows customers to simplify their infrastructure whether running transactional or analytic workloads, and provides a lower TCO.
Since Intel introduced the Intel Optane PMem 100 series, Lenovo and other Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) have submitted SAP Business Warehouse on HANA (BWH) benchmarks for SAP HANA Tailored Datacenter Integration (TDI) configurations, which allow SAP HANA customers to make use of existing hardware and infrastructure components.
The following benchmarks done by IBM Cloud and Lenovo compare Intel Optane PMem 100 and 200 series. The two SAP Benchmarks (SAP Certification #2021053 using SAP HANA 2.0 Benchmark Version 3 and SAP Netweaver 7.50 and #2021009 using SAP HANA 2.0 Benchmark Version 3 and SAP Netweaver 7.50) are like for like because both loaded 5.2 Billion rows using the SAP BWH benchmark and both support a 3 TB HANA database.
To interpret the results of the SAP BWH Benchmark, let's look at each of the 3 phases:
- Phase 1 (big data load). Phase 1 consists of loading a certain number of records to learn how the system performs. Lower numbers equal better performance. Every customer using SAP HANA Data Warehouse or SAP Business Warehouse runs these jobs nightly. In short: the quicker the jobs complete, the more time the system is available for users to run reports. In the illustrated example, approximately 5.2 billion records were loaded in 12,859 seconds versus 32,856 seconds with previous generation.
- Phase 2 (concurrent queries). This denotes the number of queries a system can run within an hour. The higher the number, the better the performance. Customers size SAP systems for peak performance so it can handle critical month end tasks like Finance month end close or Inventory run tasks efficiently. Intel Optane PMEM 200 series can run 4,222 concurrent queries within an hour vs. 1,911 with the previous generation.
- Phase 3 (single large complex query). This measures the time it takes to run a complex query, based on a real-world use case. The lower the number, the better the performance. The complex query took 89 seconds vs. 125 seconds with the previous generation.
TCO for 2nd generation Intel Optane persistent memory
A common metric to measure performance/price is Cost Per Terabyte for SAP HANA systems.
Cost Per Terabyte = Total BOM Cost of Database Servers / Total Memory in terabytes in all the Database Servers
Using the Lenovo Datacenter Solution Configurator, BOMs for Optane PMem 100 series, Optane PMem 200 series and DRAM-based solutions were priced:
- Config 1 : PMem 100 Series 3 TB HANA database with 2nd Gen Xeon Scalable Processors. Cost Per Terabyte is $47,600.
- Config 2 : PMem 200 Series 6 TB HANA database with 3rd Gen Xeon Scalable Processors. Cost Per Terabyte is $32,000.
- Config 3 : DRAM Based 4 TB HANA database with 3rd Gen Xeon Scalable Processors. Cost Per Terabyte is $57,300.
From the results, the Intel Optane PMem 200 series (Config 2 above) has 34% lower Cost Per Terabyte compared to an all DRAM system (Config 3).
New Prowess Consulting report
Prowess Consulting performed a TCO analysis for Lenovo ThinkSystem SE650 V2 and SE860 V2 servers with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors and Intel Optane PMem 200 Series against competitive offerings from Dell and HPE. The configurations varied from 4 TB to 9 TB with DRAM/PMem ratios of 1:1 and 1:2. The study compared both the CapEx to acquire systems in addition to the OpEx associated with running those solutions over a three-year period.
In addition to highlighting the TCO benefits of Lenovo's highly reliable and high performance systems, the study also showed the TCO differences between Intel Optane PMem 100 and 200 series when the competitor did not have a system with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors.
One example of that was with 4-socket servers, where the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR860 V2 with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and Intel Optane PMem 200 series was compared to the Dell EMC™ PowerEdge™ R940 with 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors and Intel Optane PMem 100 series. As shown in the chart below, the TCO of the SR860 V2 was 40% lower in a 6 TB 1:1 configuration and 35% lower in a 9 TB 1:2 configuration.
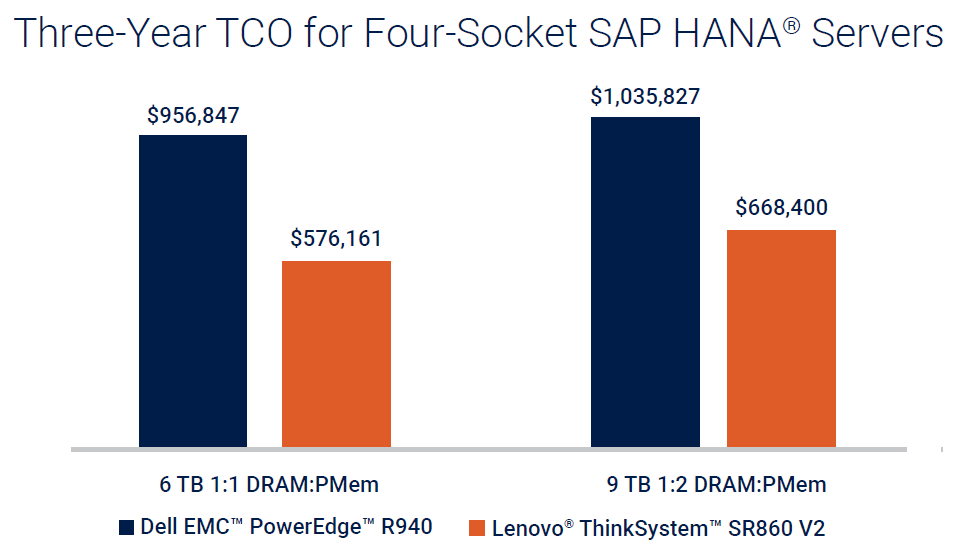
Figure 1. Greater concentrations of DIMM-based memory correlate to better three-year TCO for four-socket Lenovo ThinkSystem SR860 V2 servers, compared to Dell EMC PowerEdge R940 servers
The Prowess study assumed the average customer had a 3 system landscape (Production/High Availability/Disaster Recovery).
The greatest expense in the 3-year comparison was the compute cost, where Lenovo had a slight advantage over the competition. Where Lenovo shined, though, was in server reliability. For eight years in a row, Lenovo has led the industry in x86 server reliability according to ITIC with the least amount of unplanned downtime.
To see the full Prowess Consulting report, please click here.
Conclusion: The benefits are measurable
Lenovo systems with 3rd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable Processors and Intel Optane PMem 200 Series provide many benefits to customers. The combination provides double the performance (over the previous generation) for Phase 1 and Phase 2 of the SAP BWH benchmarks – reaching 99.4% of the performance of systems with all DRAM. And with the increased memory density of the Intel Optane PMem 200 series, Lenovo 2-socket systems like the ThinkSystem SR650 V2 can support SAP HANA databases up to 6 TB and provide a 34% lower cost per terabyte compared to previous generation systems.
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ThinkSystem®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Intel®, the Intel logo, Intel Optane®, and Xeon® are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
IBM® and IBM Cloud® are trademarks of IBM in the United States, other countries, or both.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
Configure and Buy
Full Change History
Course Detail
Employees Only Content
The content in this document with a is only visible to employees who are logged in. Logon using your Lenovo ITcode and password via Lenovo single-signon (SSO).
The author of the document has determined that this content is classified as Lenovo Internal and should not be normally be made available to people who are not employees or contractors. This includes partners, customers, and competitors. The reasons may vary and you should reach out to the authors of the document for clarification, if needed. Be cautious about sharing this content with others as it may contain sensitive information.
Any visitor to the Lenovo Press web site who is not logged on will not be able to see this employee-only content. This content is excluded from search engine indexes and will not appear in any search results.
For all users, including logged-in employees, this employee-only content does not appear in the PDF version of this document.
This functionality is cookie based. The web site will normally remember your login state between browser sessions, however, if you clear cookies at the end of a session or work in an Incognito/Private browser window, then you will need to log in each time.
If you have any questions about this feature of the Lenovo Press web, please email David Watts at dwatts@lenovo.com.
