Abstract
Unique Intel features and capabilities are only available with the third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors. These are the processors used in the new Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers. This article introduces four of these unique features and capabilities.
Introduction
Intel is providing some unique features and capabilities only available with the third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors. These are the processors used in the new Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers. Let’s take a look at some of the features and capabilities.
1. Faster CPU Throughput with 6 Intel UPI
Providing 6 Intel UPI (Intel Ultra Path Interconnect) connections for increased CPU I/O throughput is only available with third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors used in the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers.
Intel Ultra Path Interconnect provides a high performance point-to-point connection between processors in a multi-processor server. The third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors for SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 double the number of UPI connections between the processors from 3X to 6X.
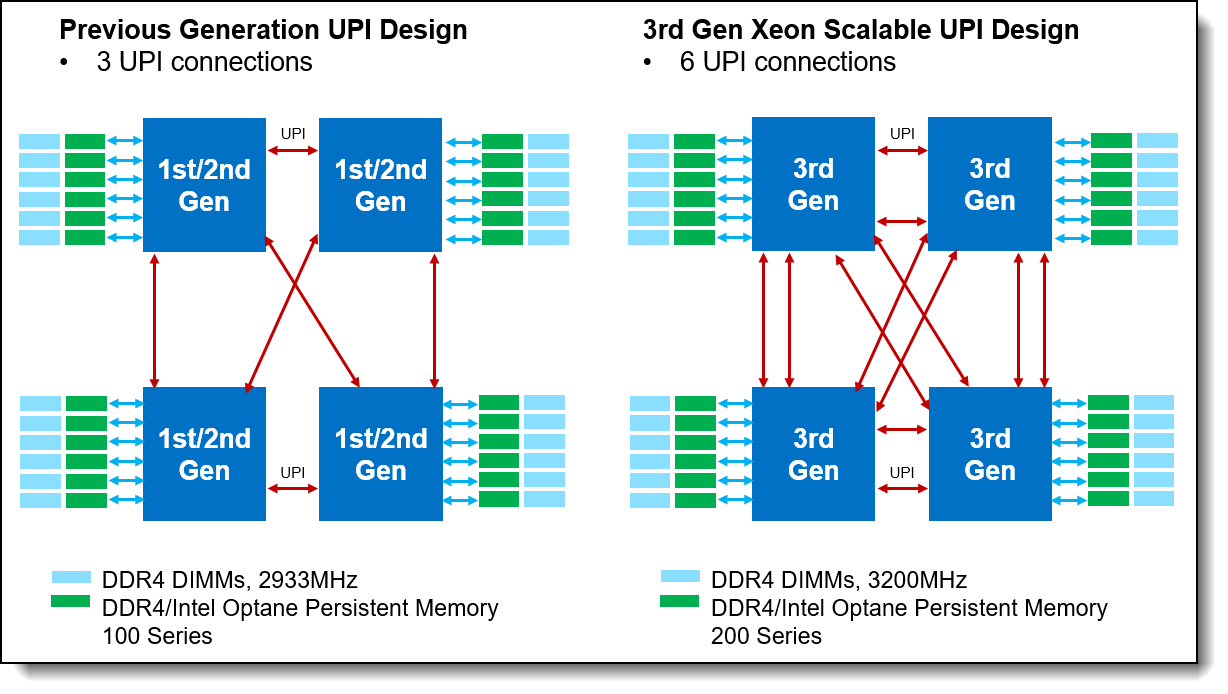
Figure 1. Comparing the UPI connections
As you can see in the figure, the 6 Intel UPIs provide double the interconnects between each processor and its memory. With the number of Intel UPI links doubled from 3 to 6, the SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 double remote bandwidth support from previous generations. This will greatly improve performance for workloads with high memory bandwidth demand and not highly NUMA(1) optimized
Large amounts of data can be transferred on the Intel UPI links between processors, the links themselves can become a performance bottleneck when the data demand rate exceeds the available Intel UPI link bandwidth. This occurs most often when running workloads that are not highly NUMA(1) optimized and when those workloads have a high demand for data between Local and Remote processors. The SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 doubles the number of Intel UPI links between processors compared to the previous generation of servers which increases the available Intel UPI bandwidth. The increased bandwidth reduces the probability that Intel UPI bottlenecks will occur when running workloads that are not NUMA optimized.
(1) NUMA:
Modern servers often have multiple processors each with its own directly attached memory. This design creates separate a memory domain for each processor. A processor can access its directly attached memory, i.e. memory in that processor’s local memory domain, faster than it can access memory in a remote processor’s memory domain. This is because memory accesses to a remote processor’s memory domain are transmitted across the processor interconnect fabric which increases memory latency. Because memory accesses from any processor can have different or non-uniform access times depending on which memory domain has the data being requested, these server memory designs are referred to as non-uniform memory access or NUMA.
All modern operating systems have some degree of NUMA awareness as do applications that manage their memory space such as database server applications. This NUMA awareness does not guarantee that all memory accesses occur to a processor’s local memory domain. A common reason is that the size of the data set being accessed by the processors is much larger than the size of a single processor’s local memory domain. So remote memory accesses might be unavoidable. Some applications can experience a higher degree of NUMA optimization by mostly or completely accessing memory local to each processor. These applications are designed or can be tuned in such a way that memory accesses from application threads running on each processor are directed to the processor’s local memory domain. These highly NUMA optimized applications generally see better performance scaling on multi-processor servers since the additional latency of remote memory
2. Faster Memory Speeds
Fast 3200 MT/s memory is available with third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors used in the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers. The new 3200 MT/s memory increases memory bandwidth by up to 12% compared to 2933MT/s memory.
Faster RAM speeds support higher memory bandwidth allowing systems to access data quicker, giving your system a boost in processor performance. Memory bandwidth hungry applications like HPC, traditional and in-memory databases and applications that stream data from storage into memory will benefit the most from the improved memory subsystem performance.
3. AI Acceleration with BFloat16
Built in AI acceleration capabilities are only available with the third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors used in the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers.
BFloat16 (BF16) is a new floating-point format that can accelerate machine learning (deep learning training, in particular) algorithms. BF16 is designed to accelerate Deep Learning Training and Inference for AI models on Image Recognition, Object Detection, Recommendation Engines, Speech Recognition and Machine/Language Translation.
BFloat16 uses 16-bit data type to represent values with similar dynamic range and accuracy of FP32 data type (Floating Point 32-bit). By doing this, it reduces memory footprint requirement and increase performance significantly for AI deep learning and training applications.
New Intel Xeon Platinum 8300H and Gold 6300H/5300H processors will support BFloat16 integration optimization in popular Frameworks.
- TensorFlow – open-sourced software library for dataflow and differentiable programming across a wide range of tasks.
- PyTorch – open-source machine learning used for application such as computer vision and natural language processing.
- OpenVINO – free toolkit facilitating the optimization of deep learning models
4. Intel Optane Persistent Memory 200 Series
The third generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors used in the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers support the next generation persistent memory (Pmem). The Intel Optane persistent memory 200 series enables unprecedented memory capacity and the fastest access to persistent memory, delivering up to 4.5TB of memory per socket. (6x 512GB Pmem 200 series plus 6x 256GB DDR4 DRAM).
Figure 2. Persistent memory installed in an SR850 V2 server
Unlike conventional DDR memory, Intel Optane persistent memory retains its data even if power is unexpectedly lost and much provides faster CPU access to persistent data than reading from a NAND SSD.
The primary targeted application for the PMem 200 Series is SAP HANA. SAP HANA was the first application to take full advantage of this PMem 100 Series capabilities using App Direct mode, allowing the column store of HANA to now reside in persistent memory. On top of the known benefits for faster restart in the case of business continuity requirements, it is possible to store more data of the column store part of SAP HANA in memory when using a combination of DRAM and persistent memory. Additionally, bigger SQL queries can be addressed to the database.
New persistent memory modules available with SR850 V2 and SR860 V2:
- Intel Optane PMem 200 Series - 128GB
- Intel Optane PMem 200 Series - 256GB
- Intel Optane PMem 200 Series - 512GB
Conclusion
Only servers supporting the Third Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors can take advantage of these unique features. The new ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 incorporates these new processors and the associated new features.
About the author
Randall Lundin is a Senior Product Manager in the Lenovo Infrastructure Solution Group. He is responsible for planning and managing ThinkSystem servers. Randall has also authored and contributed to numerous Lenovo Press publications on ThinkSystem products.
This article is one in a series on the ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2 servers:
- Five Highlights of the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR850 V2
- Five Highlights of the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR860 V2
- Why Scale-Up With 4S and 8S Servers?
- Unique Intel Features Available with ThinkSystem SR850 V2 and SR860 V2
- ThinkSystem SR860 V2 is the New 4S Performance Leader
- The Value of Refreshing Your 4-Socket Servers with the ThinkSystem SR860 V2 and SR850 V2
- The Perfect 4-Socket and 8-Socket Servers for SAP HANA
- Total Cost of Ownership Comparison of Running SAP HANA on Lenovo ThinkSystem Servers
Related product families
Product families related to this document are the following:
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ThinkSystem®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Intel®, the Intel logo, Intel Optane®, OpenVINO®, and Xeon® are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
