Authors
Updated
24 Nov 2025Form Number
LP2100PDF size
16 pages, 1.6 MBAbstract
The Veeam Hardened Repository is a secure storage location where server backups can be stored immutably for a configured amount of time. With the Hardened Repository, Veeam provides a WORM (write once, read many) storage option for Veeam backups. This role can be deployed on a general-purpose Linux server, without locking you down to the special proprietary hardware.
Lenovo recommends the ThinkSystem rack servers as excellent servers for small businesses up to large enterprises that need industry-leading reliability, management, and security, as well as maximizing performance and flexibility for future growth. The servers are designed to handle a wide range of workloads, such as databases, virtualization and cloud computing, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), infrastructure security, systems management, enterprise applications, collaboration/email, streaming media, web, and HPC.
This document provides essential post-sales information to understand the ThinkSystem rack servers basic guidelines when installing the Veeam Hardened Repository Appliance software.
Change History
Changes in the November 24, 2025 update:
- Added information about SR630 V4 and SR650 V4
- Added resources related to V4 server models configuration
Introduction to Veeam Hardened Repository
 Achieve radical resilience that can only come from complete confidence in your protection, response and recovery. Built on the principles of Data Security, Data Recovery and Data Freedom, Veeam Data Platform provides the confidence you need to take a stand against cyberattacks.
Achieve radical resilience that can only come from complete confidence in your protection, response and recovery. Built on the principles of Data Security, Data Recovery and Data Freedom, Veeam Data Platform provides the confidence you need to take a stand against cyberattacks.
- Detect and identify cyberthreats
- Respond and recover faster from ransomware
- Secure and compliant protection for your data
Key capabilities include:
- Early threat detection: AI-powered, built-in Malware Detection Engine performs low-impact inline entropy and file-extensions analysis during backup for immediate detection.
- Avoid reinfection: Content analysis helps pinpoint identified ransomware strains to prevent the reintroduction of malware into your environment.
- Guarantee survival: Prevent accidental or malicious deletion or encryption of backups by employing a zero-trust architecture, “Four-Eyes” admin protection and immutable backups.
- Proactive threat hunting: Backup anomalies are instantly reported into ServiceNow and other SIEM tools of your choice, so you can immediately perform triage and reduce further risk to your data.
- Automate clean recovery: Perform orchestrated recovery of an entire environment using malware-free restore points.
- Verify security and compliance: Ensure recovery success with automated scans using the Security & Compliance Analyzer, leveraging infrastructure hardening and data protection best practices.
- Get a second opinion: Let your cyberthreat tool report infections directly into the Veeam Incident API, marking existing restore points as infected or trigger backup
- Recover with precision: Perform point-in-time recovery to the moment prior to infection with the I/O Anomaly Visualizer, ensuring the lowest possible data loss thanks to Veeam CDP.
- Put the spotlight on malware: Highlight threats, identify risks and measure the security score of your environment in the Veeam Threat Center.
Detailed guidance on the Hardened Repository is available in the Version 12 and Version 13 documentation.
Introduction to the recommended Lenovo ThinkSystem Servers
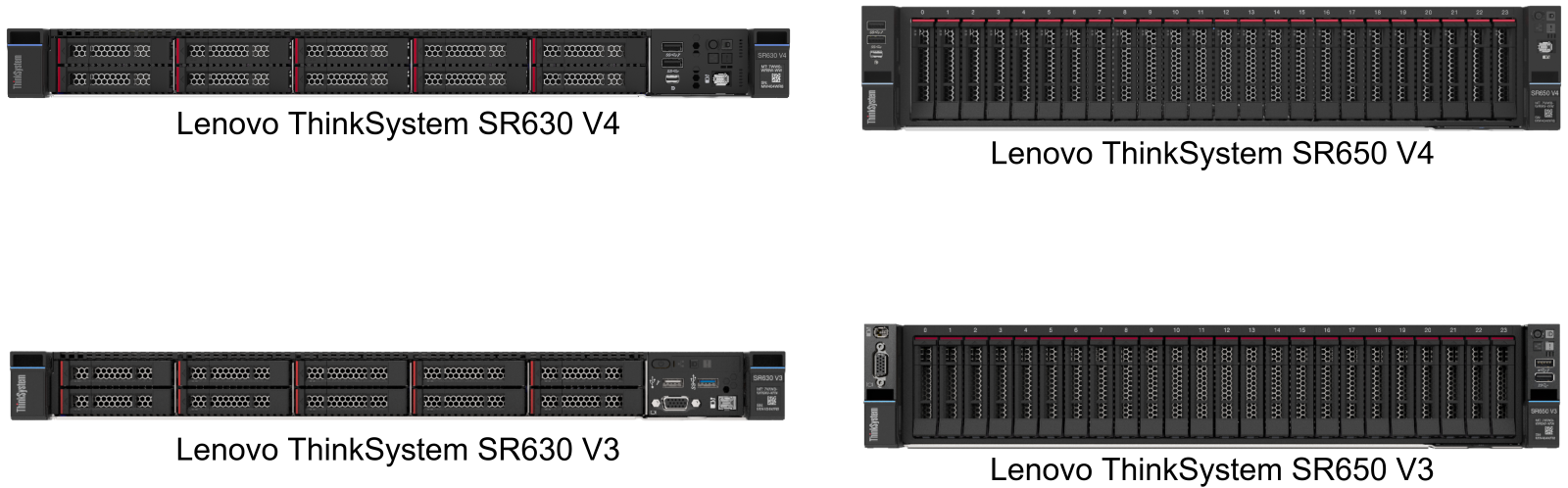
Combining performance and flexibility, the Lenovo ThinkSystem rack servers are a great choice for enterprises of all sizes. These servers offer a broad selection of drive and slot configurations and offers numerous high-performance features. Outstanding reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS) and high-efficiency design can improve your business environment and can help save operational costs.
Figure 1. Recommended Lenovo ThinkSystem Servers for Veeam Hardened Repository deployment
For more information about the supported servers, see the following Lenovo Press product guides:
The Red Hat hardware certification list (HCL) pages for the servers are as follows:
- Red Hat Certification for SR630 V4, Red Hat Certification for SR650 V4
- Red Hat Certification for SR630 V3, Red Hat Certification for SR650 V3
Server documentation links:
Firmware update procedures
Updating the firmware and drivers on a regular schedule is the recommended best practice for several reasons:
- Achieves the highest-level hardware availability
- Enables you to proactively apply the latest bug fixes before your systems are affected by them
- Increases security, compatibility, and system uptime
For guidance on how to update the firmware of Lenovo ThinkSystem V3 and V4 servers, see the following documents:
Recommendations for updates
To have a successful firmware update consider these recommendations:
- Use of UpdateXpress System Packs
- Lenovo recommends that you update the entire system to the latest UpdateXpress System Pack (UXSP) level before you deploy the server into a production environment. This includes system firmware, all adapter and hard-drive firmware, and the corresponding device drivers in the operating system.
Tip: Install all the hardware components (modules, adapters, and drives) and power on the system at least once before updating the entire system, so that everything will be activated, detected, and updated together.
Installing system firmware
If new system management controller firmware (IMM or XCC) is applied, either a system management controller restart (via the XCC/IMM web interface or CLI) or a full power cycle (unplug the server) will be required to activate the pending updates. A virtual reseat will also restart the controller (if the function is available in your server).
If new UEFI firmware is applied, a server reboot is required to activate the updates. If delayed activation is being used, such as in XClarity Administrator, then the updates will remain as pending (unapplied) on the system until server is restarted.
If the system management controller firmware update package also includes updated FPGA firmware (as indicated in the change history for the update), then both the system management controller will need to be restarted (via XCC/IMM web interface/CLI) and the server will need to be rebooted before the FPGA change becomes effective. A full power cycle (unplug the server) will achieve both.
Additional recommendations
Some additional recommendations when applying firmware updates:
- When installing new hardware
If you install or upgrade hardware components later, make sure that you perform a full system update to ensure that the system can handle the new hardware, and that the newly installed components have the proper firmware and drivers.
- Updating firmware manually
If you are updating individual firmware manually or via your own script but are not using the XClarity tools mentioned above, you should always update the BMC (XCC or IMM) first, restart the BMC and wait 5 minutes, then update UEFI, reboot the server, then update the rest of the system. This order ensures that critical dependencies are satisfied.
- Subscribe to updates on the Lenovo support site
Make sure that you visit the Lenovo Support web site regularly, or that you subscribe to product notifications to be informed of critical updates for your devices. Then, plan your maintenance schedule accordingly.
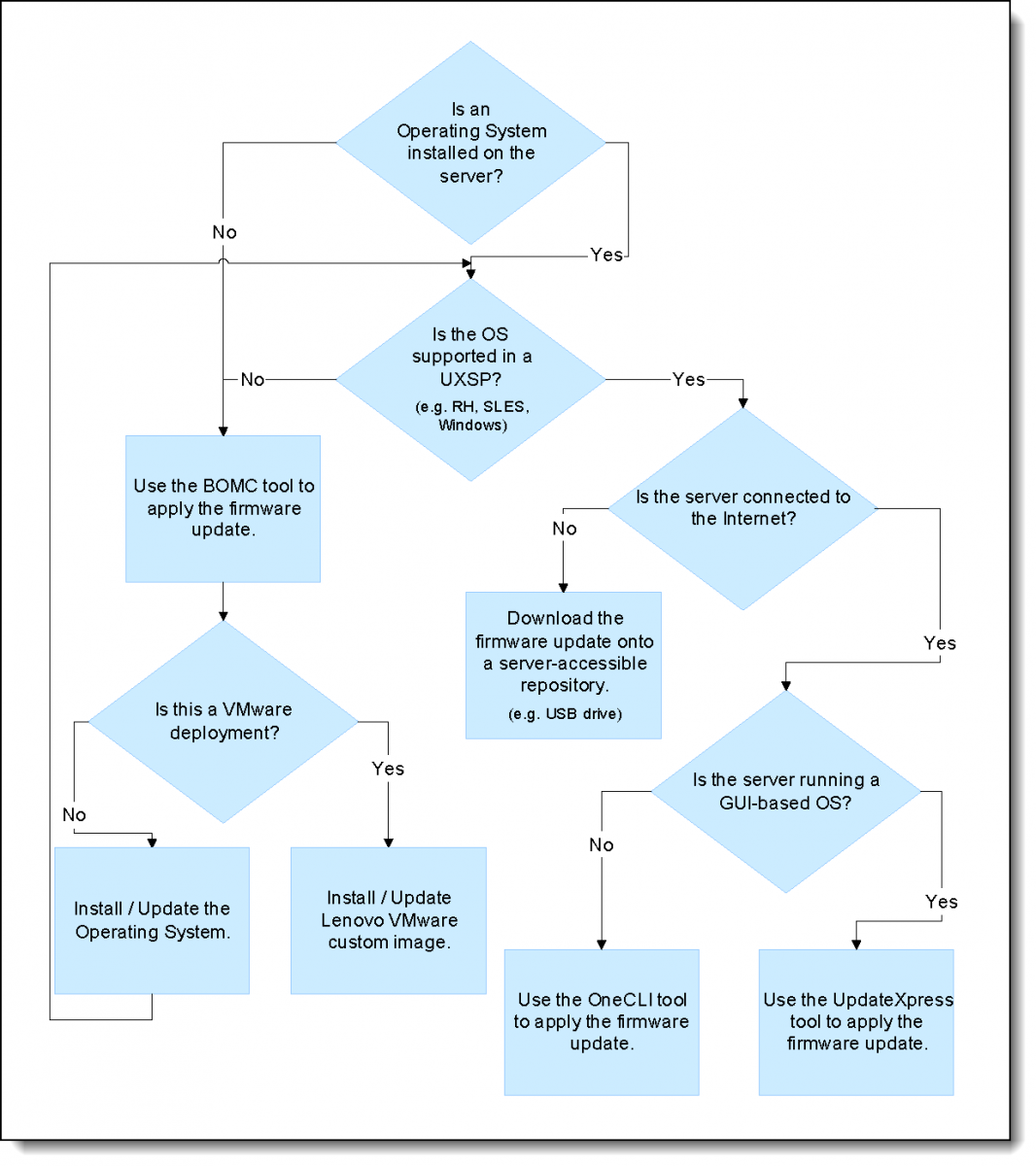
Update process flow
Use the following flow chart to determine the best tool to be used when updating the firmware and device drivers, based on your environment.
You could also follow this interactive guideline in our Youtube Channel: How to update firmware on Lenovo XClarity controller
RAID setup for logical drives
For information on setting up RAID arrays, see the following pages on the Lenovo Docs web site:
- SR630 V4 RAID Configuration, SR650 V4 RAID Configuration
- SR630 V3 RAID Configuration, SR650 V3 RAID Configuration
Using RAID to store data remains one of the most common and cost-efficient methods to increase server's storage performance, availability, and capacity. Supported RAID levels varies by the storage controller configured in the server.
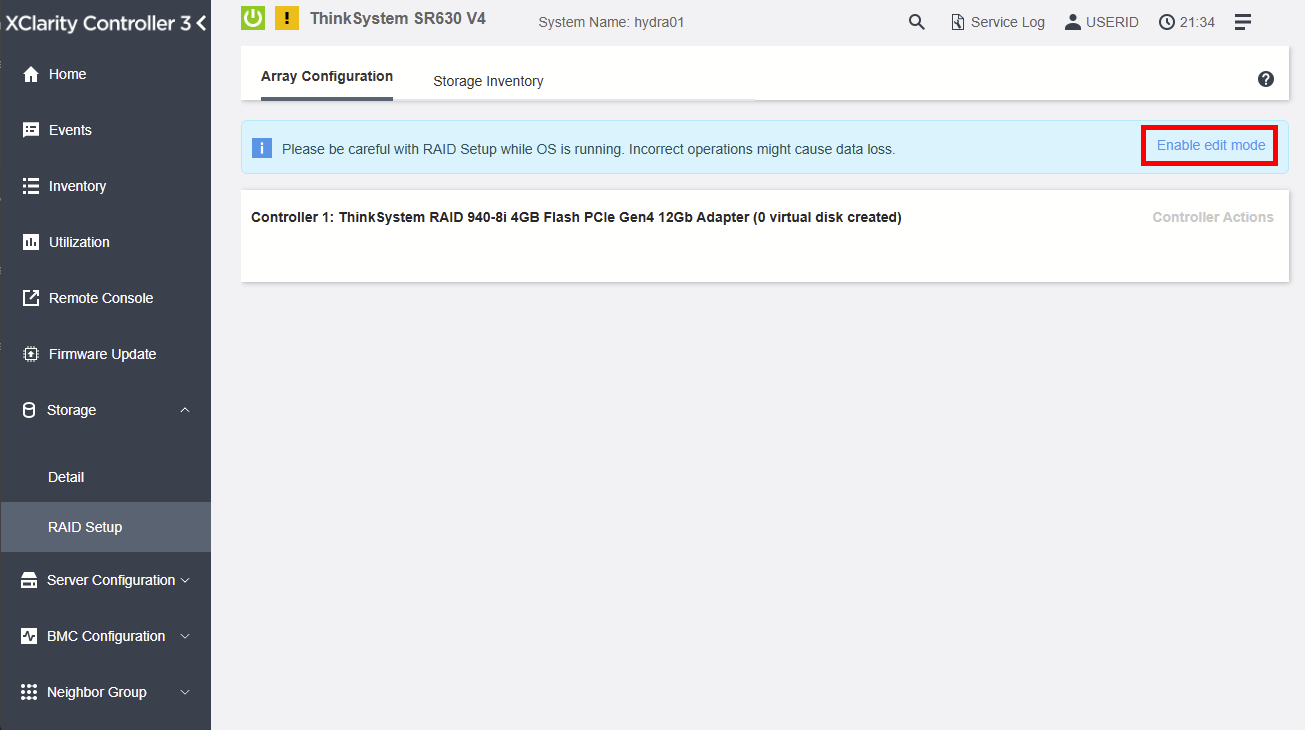
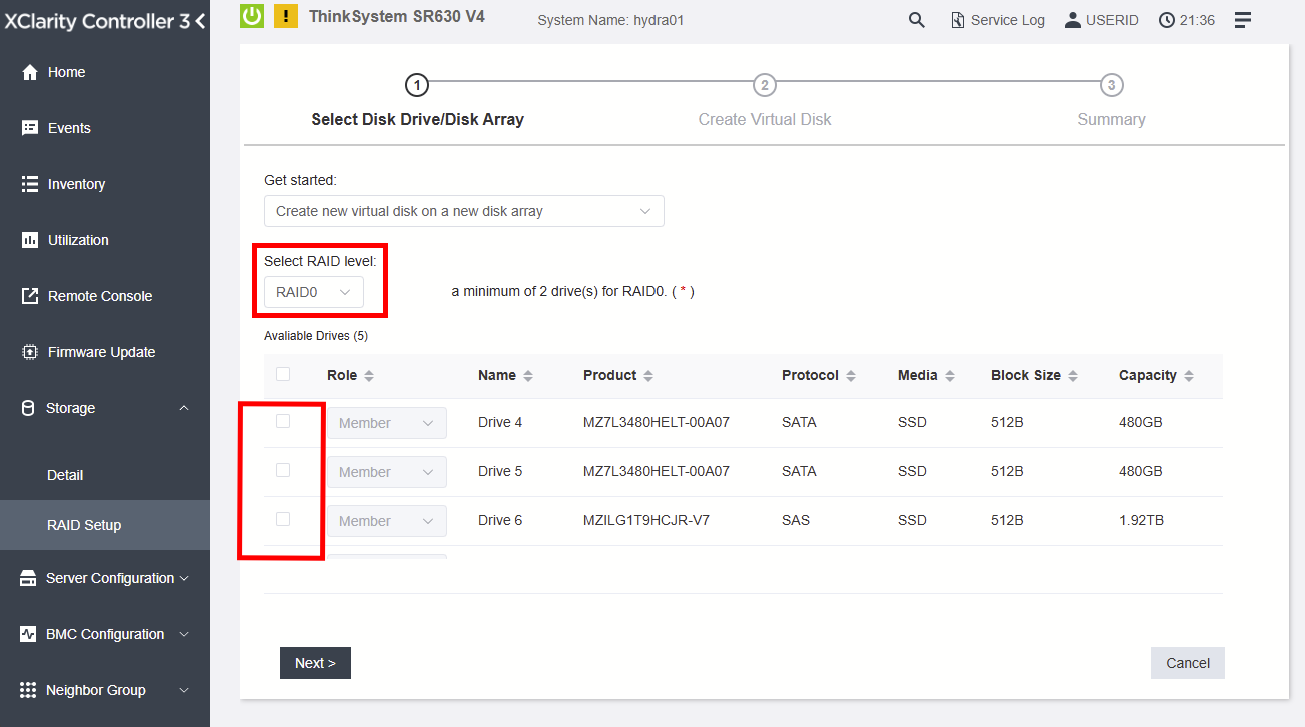
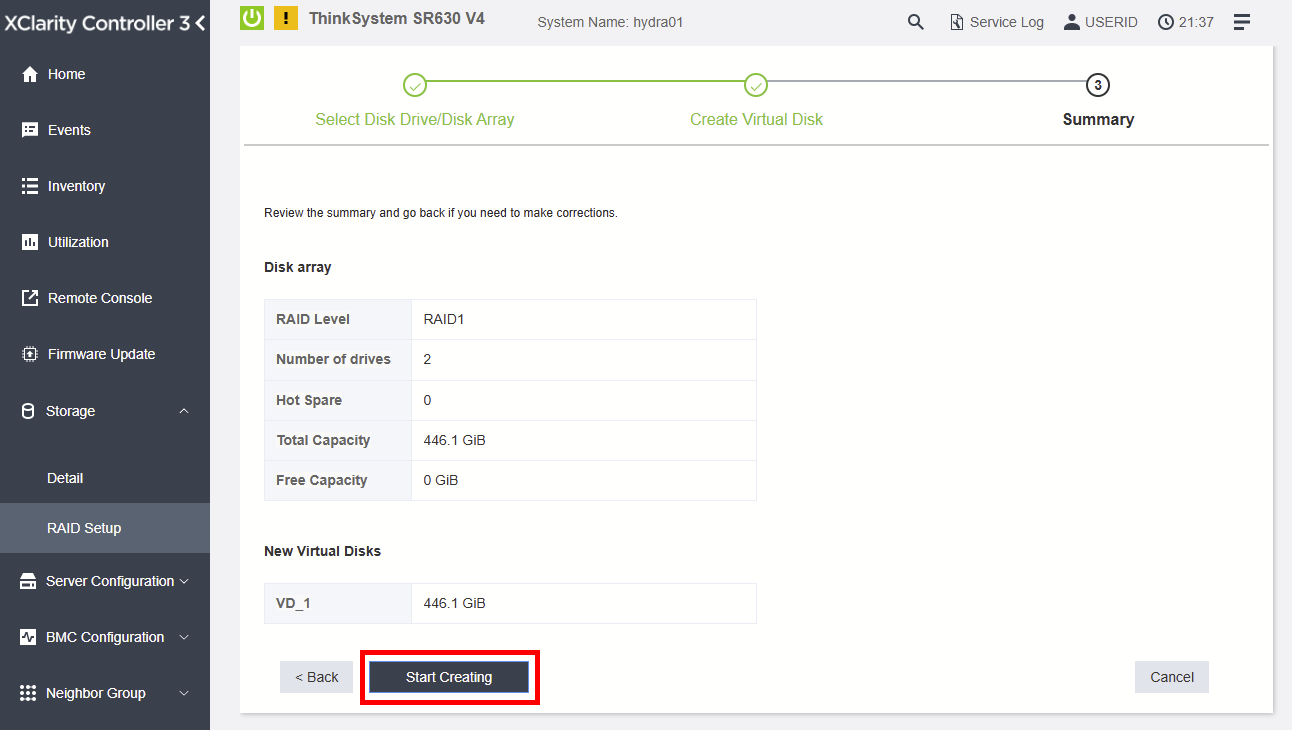
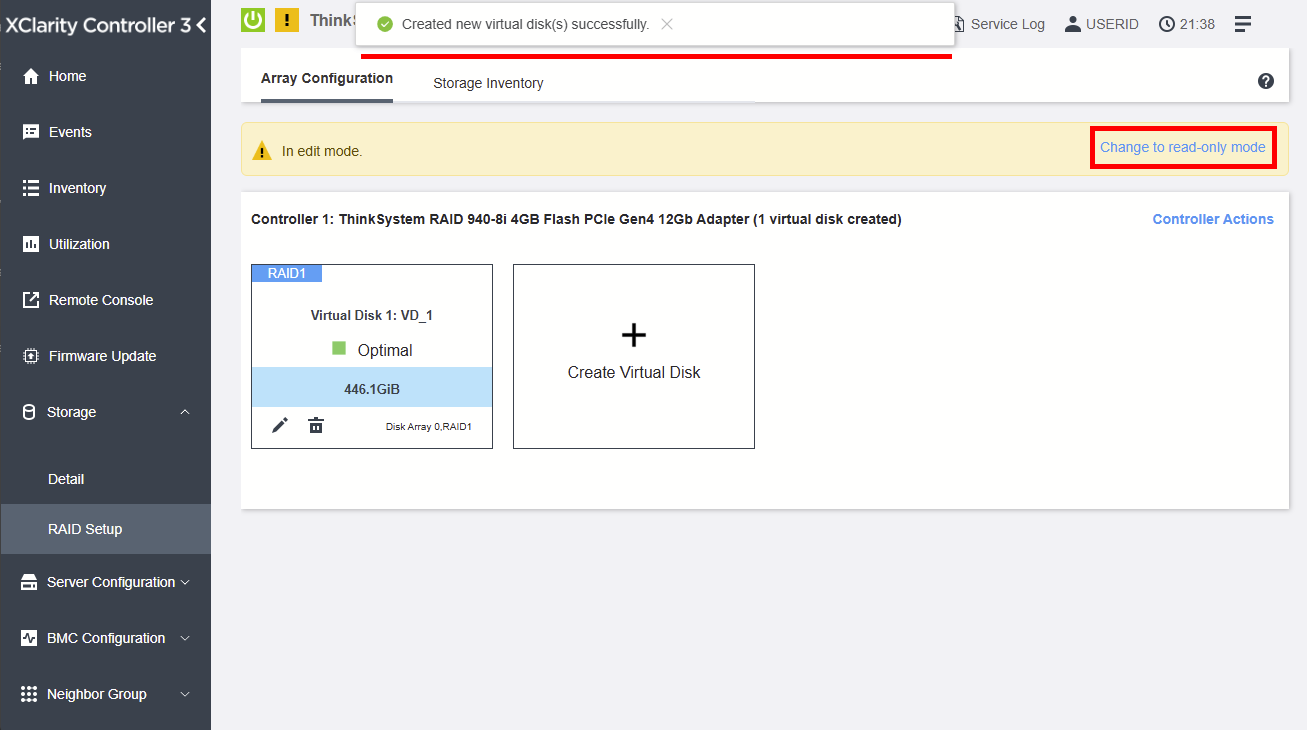
To create a RAID array in the XCC web interface, access the RAID Setup from Storage and follow the detailed procedure below.
Figure 3. Click "Enable edit mode" button
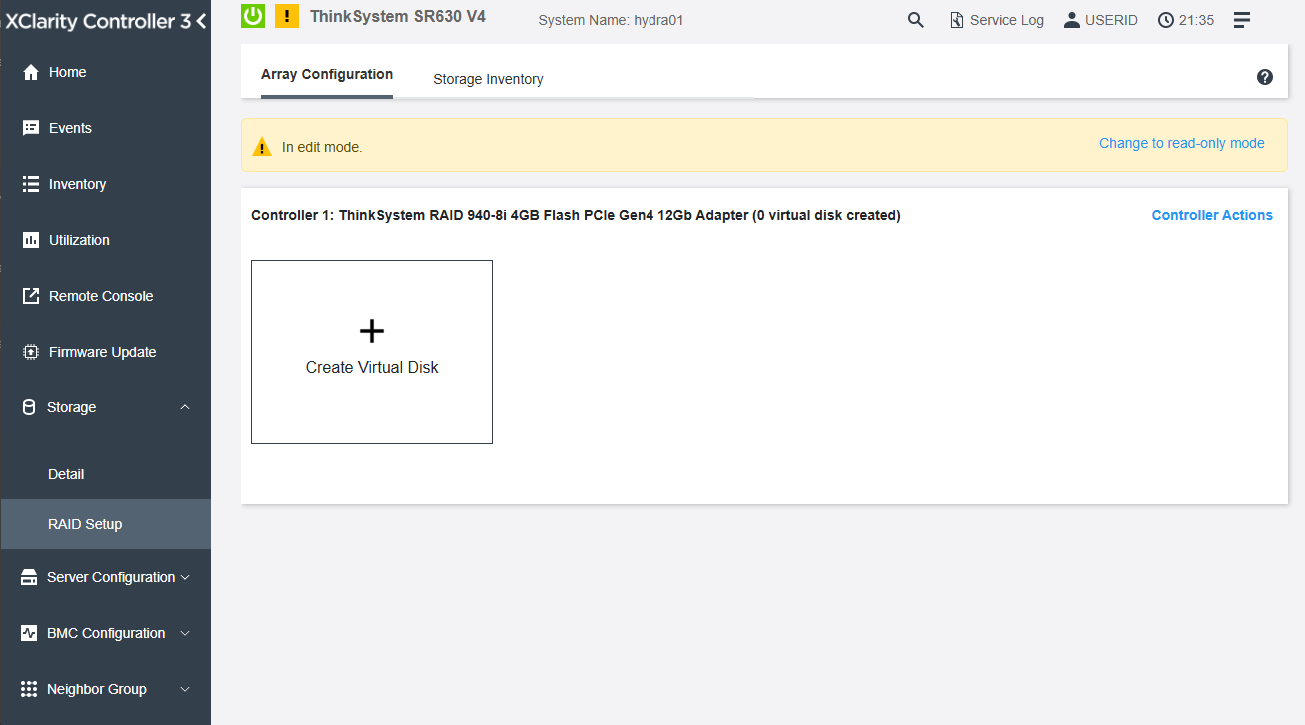
Figure 4. Click "Create Virtual Disk" button
Figure 5. Select the desired RAID level and choose the disks to be used by the RAID array
Figure 6. Click "Start Creating" button
Figure 7. After the successful RAID creation, a message will be shown. Click "Change to read-only mode" to exit the editing mode.
You can configure RAID on the servers using Lenovo XClarity Provisioning Manager (LXPM).
Check LXPM V4 for V3 server models and LXPM V5 for V4 server models.
You can also configure RAID on these servers using the XClarity Controller Web UI.
Check XCC2 Web UI storage configuration for V3 server models and XCC3 Web UI storage configuration for V4 server models.
The XCC Command Line Interface also supports RAID configuration.
Check XCC2 CLI documentation for V3 server models and XCC3 CLI documentation for V4 server models.
Security procedures
To ensure your server is secure, following the guidance in the following paper:
How to Harden the Security of your ThinkSystem Server and Management Applications
https://lenovopress.lenovo.com/lp1260-how-to-harden-the-security-of-your-thinksystem-server
Topics in the paper:
- Hardening UEFI
- Hardening Lenovo XClarity Controller
- Hardening Lenovo XClarity Administrator
- Hardening Lenovo XClarity Orchestrator
XClarity Redfish integration
The Lenovo XClarity Controller provides a Redfish compliant set of easy-to-use REST APIs that can be used to access Lenovo XClarity Controller data and services from applications running outside of the Lenovo XClarity Controller framework.
This allows for easy integration of Lenovo XClarity Controller capabilities into other software, whether the software is running on the same system as the Lenovo XClarity Controller server, or on a remote system within the same network. These APIs are based on the industry standard Redfish REST API and are accessed via the HTTPS protocol.
Check XCC2 REST API for V3 server models and XCC3 REST API for V4 server models to learn more about Lenovo XClarity Controller Redfish REST API.
Lenovo provides open-source sample Redfish scripts that can be used as reference for developing software that communicates with Lenovo Redfish REST API. These sample scripts can be found here:
- Python: https://github.com/lenovo/python-redfish-lenovo
- PowerShell: https://github.com/lenovo/powershell-redfish-lenovo
DMTF specifications related to the Redfish API are available at: https://redfish.dmtf.org/. This website provides general specifications and other reference material on the Redfish REST API.
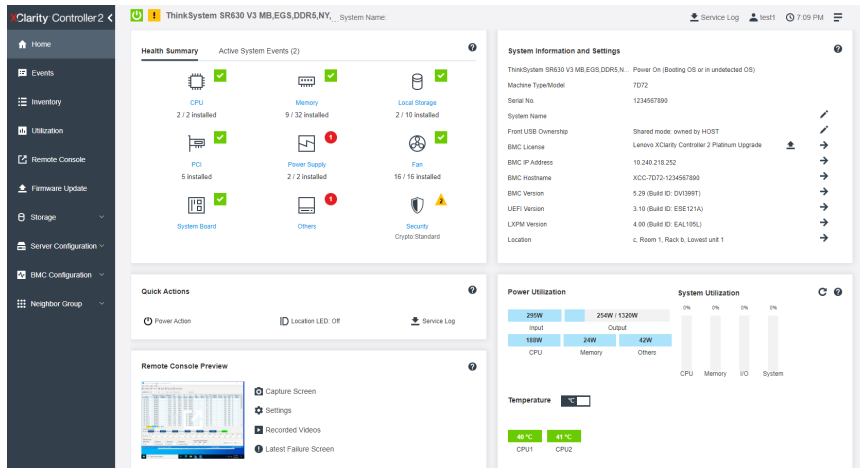
Alternative health monitoring using XCC
The XClarity Controller UI offers a system status page where you can view the server hardware status, event and audit logs, system status, maintenance history and alert recipients.
The following documentation links describe the available functions.
- Viewing the Health Summary/Active System Events
Use the information in this topic to understand how to view the Health Summary/Active System Events. - Viewing the System Information
This topic explains how to obtain a summary of common server information. - Viewing the System Utilization
By clicking Utilization in the left pane, a summary of common server utilization information is provided. - Viewing Event Logs
The Event Log provides a historical list of all hardware and management events. - Viewing Audit Logs
The Audit Log provides a historical record of user actions, such as logging in to the XClarity Controller, creating a new user, and changing a user password. - Viewing the Maintenance History
The Maintenance History page includes information about the firmware update, configuration and hardware replacement history. - Configuring Alert Recipients
To add and modify email and syslog notifications or SNMP TRAP recipients, use the information in this topic. - Capturing the latest OS failure screen data
Use the information in this topic to capture and view an operating system failure screen.
XClarity use of remote console for ISO installation
For guidance, see the following page in the Lenovo documentation, Enabling the remote console functionality.
XClarity Controller remote console functionality is available only in the XClarity Controller Advanced and XClarity Controller Enterprise features. If you do not have the privilege to operate the remote console, you will see a lock icon.
After you have purchased and obtained the activation key for the XClarity Controller Advanced upgrade install it using the instructions under Installing an activation key.
To use the remote console functionality, complete the following steps:
- Click the image with a white diagonally pointing arrow in the Remote Console section of the XClarity Controller homepage or the Remote Console web page.
- Select one of the following modes:
- Start remote console in single-user mode
- Start remote console in multiuser mode
- Select whether or not to allow others to request to send a disconnection request to a remote console user when someone wishes to use the remote console feature and the feature is already in use in Single User Mode, or when the maximum number of users are using the remote console feature in Multi User Mode. The No response time interval specifies how long the XClarity Controller will wait before automatically disconnecting the user if no response is received to the disconnection request.
- Select whether or not to allow record the latest three server boot videos, to allow record the latest three server crash videos, and to allow OS failure screen capture with HW error.
- Click Launch Remote Console to open the remote console page in another tab. When all possible remote console sessions are in use, a dialog box will pop up. From this dialog box, the user can send a disconnection request to a remote console user who has enabled the setting to Allow others to request my remote session disconnect. The user can accept or deny the request to disconnect. If the user does not respond within the interval specified by the No response time interval setting, the user session will automatically be ended by the XClarity Controller.
For more information
For more information about Veeam offerings from Lenovo, see the Veeam Software Solution Product Guide.
Authors
Edgar Rodriguez is the Global Alliance Manager for Cyber Resiliency Partners at Lenovo. With over 15 years of experience in the technology sector, Edgar drives the strategic partnership between Lenovo and data protection partners. He has a customer-centric and data-driven approach to ensure our global go-to-market efforts always start with the customer, their challenges, priorities, and words. He works cross-functionally and collaboratively to craft compelling messaging, coordinate cross-organizational teams, implement best practices, to set Lenovo apart from the competition. He is passionate about understanding why people buy life-changing products and how these products get into their hands, always thinking on customer journeys, feelings, and insights.
Natalie Zielinski serves as a Product Marketing Specialist within Lenovo’s Infrastructure Solutions Group (ISG). In her role, she specializes in developing and managing content that highlights the value of Lenovo’s partnerships within the Software Ecosystem. By crafting impactful collateral, Natalie showcases how these collaborations drive innovation and deliver cutting-edge solutions to customers worldwide. Since joining Lenovo in 2023, Natalie has been working in marketing, bringing creative strategies to elevate partner engagement. Her work reflects a commitment to amplifying the significance of these partnerships and positioning Lenovo as a leader in the tech industry.
Trademarks
Lenovo and the Lenovo logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both. A current list of Lenovo trademarks is available on the Web at https://www.lenovo.com/us/en/legal/copytrade/.
The following terms are trademarks of Lenovo in the United States, other countries, or both:
Lenovo®
ThinkSystem®
XClarity®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Linux® is the trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
PowerShell is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
Configure and Buy
Full Change History
Changes in the November 24, 2025 update:
- Added information about SR630 V4 and SR650 V4
- Added resources related to V4 server models configuration
First published: January 17, 2025
Course Detail
Employees Only Content
The content in this document with a is only visible to employees who are logged in. Logon using your Lenovo ITcode and password via Lenovo single-signon (SSO).
The author of the document has determined that this content is classified as Lenovo Internal and should not be normally be made available to people who are not employees or contractors. This includes partners, customers, and competitors. The reasons may vary and you should reach out to the authors of the document for clarification, if needed. Be cautious about sharing this content with others as it may contain sensitive information.
Any visitor to the Lenovo Press web site who is not logged on will not be able to see this employee-only content. This content is excluded from search engine indexes and will not appear in any search results.
For all users, including logged-in employees, this employee-only content does not appear in the PDF version of this document.
This functionality is cookie based. The web site will normally remember your login state between browser sessions, however, if you clear cookies at the end of a session or work in an Incognito/Private browser window, then you will need to log in each time.
If you have any questions about this feature of the Lenovo Press web, please email David Watts at dwatts@lenovo.com.